Flame retardant treatment of plastic wood composite materials to achieve the corresponding flame retardant level can further enhance their market value. In recent years, the synergistic effect of flame retardants and surface modification technology to improve flame retardant performance and efficiency has become a hot research topic in the academic community. There are three main methods to enhance the flame retardant performance of plastic wood composite materials: the first method is to immerse natural wood cellulose fibers together with flame retardants in an autoclave before production; The second method is to add flame retardants in liquid or solid form during the production process of composite materials; The third method is to add inorganic nanoparticles to the composite material. These three methods of introducing flame retardants are the most common, including commonly used flame retardants and their classifications.
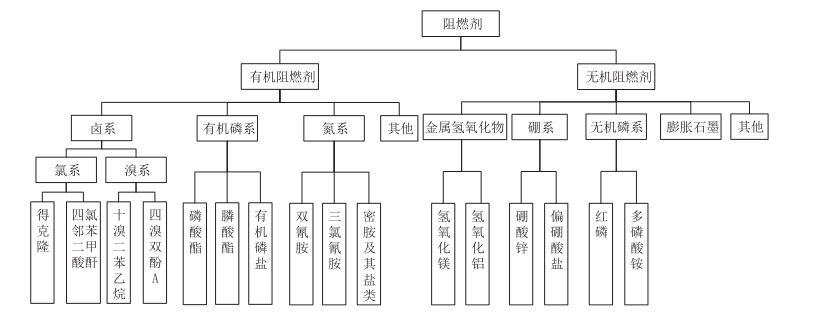
According to reports, a caffeic acid modified ammonium polyphosphate based flame retardant (MAPP-CA) was prepared using amino modified ammonium polyphosphate (MAPP) and caffeic acid (CA). The effects of two different flame retardants, ammonium polyphosphate (APP) and MAPP-CA, on the flame retardant properties of plastic wood composites were studied. The results showed that both APP and MAPP-CA endowed plastic wood composites with good flame retardant properties, and MAPP-CA had a better flame retardant effect than APP; Add inorganic flame retardants Mg (OH) 2 and Al (OH) 3 to biochar/wood/plastic composite materials and study their flame retardant properties. The results showed that both Mg (OH) 2 and Al (OH) 3 can significantly improve the flame retardant properties of the material, with Mg (OH) 2 having a better flame retardant effect than Al (OH) 3. Al (OH) 3 reduces the mechanical properties of the material, while Mg (OH) 2 can significantly improve the tensile and impact strength of the material. When the addition of Mg (OH) 2 is 40%, the flame retardant effect is the best, indicating that some flame retardants can alter the strength of the material. WANG et al. used APP as a flame retardant to carry out flame retardant treatment on foamed polyurethane/wood powder composite materials (F plastic wood composite materials), and prepared composite materials by adding and impregnating methods respectively. The results showed that the F plastic wood composite material after impregnation flame retardant treatment had better flame retardant effect, and APP enhanced the fire resistance of the F plastic wood composite material, indicating that different types of flame retardant treatment would have different effects on the material’s properties; Octaaminopropyl POSS (OA-POSS) was prepared by hydrolysis and condensation of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (KH550), and then OA-POSS/WF/PP composite materials were prepared by melt blending method. The flame retardant performance test analysis of composite materials shows that the addition of OA-POSS can increase the limit oxygen index (LOI) value of the composite material, and increasing the amount of addition will increase the LOI value of the material. The combustion experiment showed that OA-POSS can reduce the heat release rate and total heat release of the material to a certain extent, increase the residual carbon content of the composite material, but has no significant effect on reducing the smoke release of the material. The larger the amount of OA-POSS added, the better the flame retardant performance of the material.
